FASHION
Rose Gold: An In-Depth Exploration
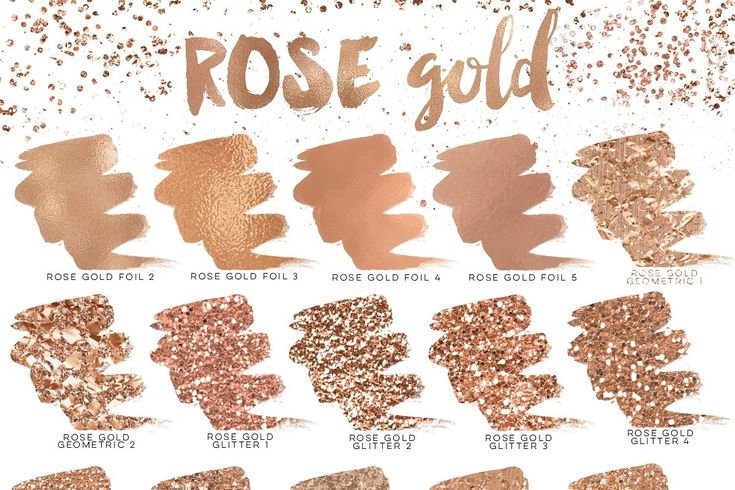

The Allure of Rose Gold: A Modern Classic
In recent years, rose gold has made a significant mark in various industries, from jewelry and fashion to technology and interior design. This captivating blend of gold and a hint of copper offers a warm, pinkish hue that has charmed its way into the hearts of many. But what is it about rose gold that makes it so irresistible?
Rose gold’s origin
Rose gold’s origin can be traced back to Russia in the early 19th century, where it was initially known as Russian gold. This alloy became popular under the creative craftsmanship of renowned jeweler Carl Fabergé, who utilized rose gold in his exquisite Fabergé eggs. Over time, the allure of its delicate and distinctive color transitioned across borders, cementing its place as a timeless and beloved option in the jewelry industry worldwide.
A Brief History of Rose Gold
Rose gold, also known as pink or red gold, first gained popularity in Russia during the 19th century, earning the moniker “Russian gold.” The alloy was initially used in jewelry, where the addition of copper to gold created a durable and eye-catching material.
Over time, rose gold found its way into Western markets, where it saw fluctuating popularity. During the 1920s’ Art Deco era, rose gold was embraced for its romantic and vintage appeal. Fast forward to the 21st century, and rose gold has become a staple in contemporary design, adored for its timeless elegance and versatility.
Types of Rose Gold
It comes in various shades, primarily determined by the proportion of copper mixed with pure gold. The different tones can range from a subtle, soft blush to a more pronounced reddish hue. These variations allow it to cater to a diverse range of preferences and styles.
-
18K Rose Gold
18K rose gold is a popular choice in the jewelry industry, combining the elegance of high-purity gold with the distinct rosy hue admired by many. This alloy consists of 75% pure gold mixed with 25% copper and sometimes silver, which imparts its signature warm, pinkish color.
-
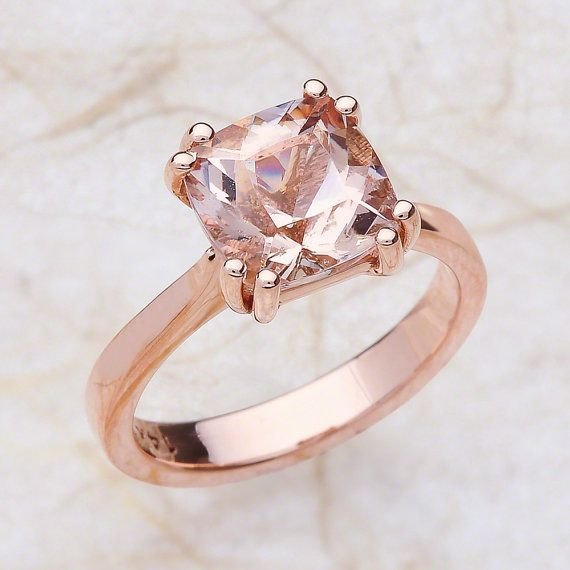
The balance of these metals contributes to both the aesthetic appeal and the material properties of 18K rose gold, making it durable yet malleable enough for intricate designs. Its luxurious appearance and elegant sheen make it a favored option for engagement rings, wedding bands, and other fine jewelry pieces.
-
The blend of gold and copper not only enhances its appearance, but also provides greater resistance to wear and tear compared to higher karat options. As a result, 18K rose gold offers an ideal balance of beauty, durability, and value, making it a treasured component in many collections.
-
14K Rose Gold:
14K rose gold is a popular choice for those seeking a balance between durability and the distinctive rosy hue. This alloy contains 58.3% pure gold, with the rest composed of copper and sometimes a small percentage of silver or other metals, which enhances its strength without compromising its beautiful color.
-
The inclusion of copper not only saturates the gold with a warm, pinkish glow, but also increases the metal’s toughness, making it suitable for everyday jewelry items like rings, bracelets, and necklaces.
-
The appeal of it lies in its ability to retain a rich color over time, while offering a more affordable alternative to higher karat golds. Its subtle elegance pairs well with various gemstones, allowing endless creative designs that suit diverse personal styles and occasions.
-
16K Rose Gold
When selecting rose gold jewelry, one can come across different karat values, such as 16K rose gold, which signifies the gold content is approximately 66.7%. This specific karat measurement involves slight variations in alloy composition, predominantly a blend of gold, copper, and silver.
-
The balance of these metals results in a durable and warm-hued alloy, balancing both aesthetics and practicality. While less common than 14K or 18K options, 16K rose gold offers a distinct middle ground, providing durability while maintaining a rich color that is hallmark to rose gold.
-
Its unique properties make it an appealing choice for consumers looking for something distinctively beautiful, yet robust for everyday wear. As with other rose gold varieties, it’s crucial to maintain it well to preserve its charming appearance and prevent potential tarnishing from copper content.
These types of it offer options suitable for different tastes, ensuring that the allure of this modern classic can be enjoyed in various ways.
Comparing Gold Alloys: A Colorful Spectrum
Gold is a versatile metal, capable of being alloyed with various elements to create a stunning array of colors, each with its own unique appeal and characteristics:
Rose Gold
This, as previously discussed, is a blend of gold and copper that results in a warm, pinkish hue. Its romantic and vintage allure makes it a popular choice for jewelry, offering both elegance and versatility.
White Gold
White gold is created by alloying gold with metals like palladium, silver, or nickel, resulting in a silvery-white appearance. It is often coated with rhodium for enhanced durability and luster. This contemporary choice is cherished for its sleek and sophisticated look, often used in wedding bands and engagement rings.
Yellow Gold
Traditional yellow gold is made by mixing pure gold with metals such as copper and zinc. Maintaining the classic golden hue, it embodies timelessness and luxury, making it a perennial favorite in jewelry design.
Red Gold
This, like metal, contains a higher proportion of copper, which imparts a rich and bold reddish tone. This striking option offers a dramatic twist on conventional gold colors.
Blue Gold
Blue gold is an intriguing alloy that incorporates metals like indium or gallium to create a bluish tint. While less common in jewelry, its unique color makes it an intriguing choice for those seeking something truly distinctive.
Black Gold
Achieving black gold involves plating traditional gold with black rhodium or ruthenium, or developing a patina through oxidation. This edgy and modern color is increasingly favored for its bold and alternative statement.
Green Gold
Green gold, also known as Electrum, is an alloy of gold and silver, sometimes with the addition of cadmium, which produces a light greenish tint. Its subtle and earthy tone offers a unique option for nature-inspired designs.
Each type of this provides different aesthetic possibilities and appeals to various tastes, showcasing the adaptability and creativity present within the world of goldsmithing.
The Science Behind the Hue
The unique color of it is achieved by blending pure gold with copper and a small amount of silver. The proportion of these metals determines the intensity of the pink hue. A typical this alloy might consist of 75% gold, 22.25% copper, and 2.75% silver. The copper content gives this its signature blush, and the silver helps soften the color, providing a subtle sheen that complements various skin tones beautifully.
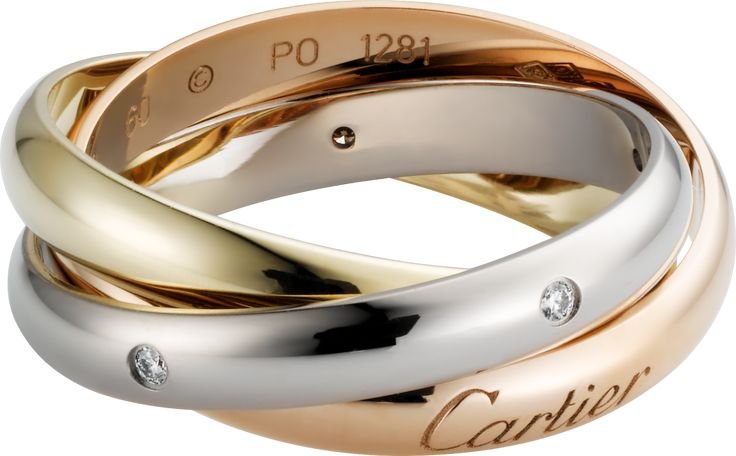
Rose Gold in Jewelry
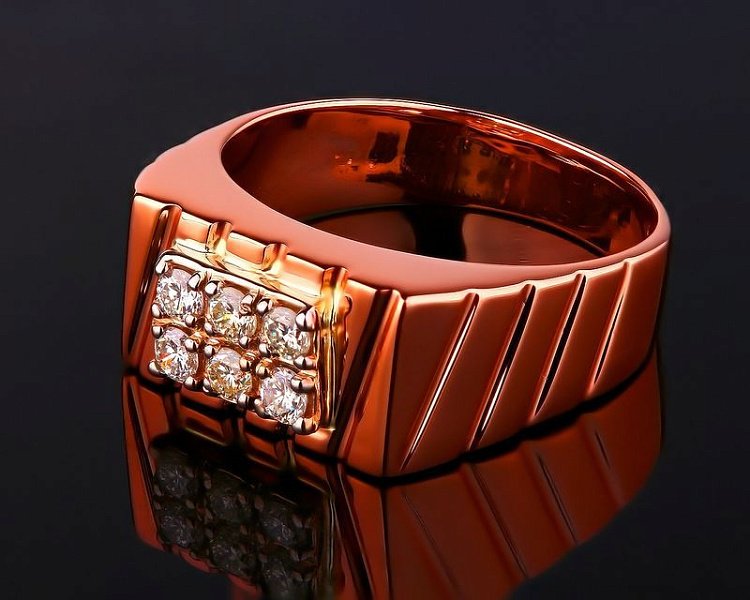
Perhaps the most well-known application of it is in the world of jewelry. The metal’s romantic hue lends itself perfectly to wedding bands, engagement rings, and everyday pieces. Its warm color enhances the brilliance of diamonds and other gemstones, creating striking contrasts and harmonious blends. Unlike traditional yellow gold, it offers a modern twist that appeals to both classic and contemporary tastes.
Rose Gold in Fashion and Beauty
It has also permeated the fashion and beauty industries. Designers often incorporate this metal accents into clothing, handbags, and accessories, adding sophistication and glamour. In the beauty sector, rose gold can be found in makeup products, such as eyeshadows, lipsticks, and highlighters, offering a flattering shade for many complexions. The color’s versatility allows it to complement a range of styles, from minimalistic to ornate.
Rose Gold in Technology
In the tech world, this metal has become a popular color choice for consumer electronics. Many leading brands offer rose gold variations of their devices, from smartphones and laptops to headphones and smartwatches. This trend reflects a growing desire for products that are not only functional, but also aesthetically pleasing.
Rose Gold in Interior Design
Interior designers have embraced this for its ability to add warmth and style to living spaces. The metal is often used in lighting fixtures, furniture, and decorative accents, providing a chic and modern feel. When paired with neutral tones or complementary colors, rose gold can turn a simple space into an elegant retreat.
The Psychology of Rose Gold
Part of this appeal lies in its psychological impact. The color pink is often associated with love, compassion, and calmness. By incorporating these attributes into a luxurious metal like gold, rose gold exudes a sense of comfort and sophistication. This combination resonates with those seeking both beauty and balance in their surroundings.
Rose Gold Prices in Different Countries and Central Asia
The price of This can vary significantly depending on market demands, local economic factors, and purchasing costs in various countries. Below is a table that provides an approximate price range for rose gold per gram in different regions, including Central Asia:
|
Country/Region |
Price per Gram (USD) |
|---|---|
|
United States |
$55 – $65 |
|
United Kingdom |
£40 – £50 |
|
Australia |
AUD 80 – AUD 90 |
|
India |
₹4,000 – ₹4,500 |
|
China |
¥360 – ¥420 |
|
Russia |
₽4,200 – ₽4,800 |
|
Kazakhstan (Central Asia) |
KZT 24,000 – KZT 28,000 |
|
Uzbekistan (Central Asia) |
UZS 650,000 – UZS 750,000 |
These values are approximate and can fluctuate based on various factors, including purity of the alloy, import taxes, and local supply and demand. It is advisable to check with local jewelers or financial experts in the respective regions for the latest pricing and trends.
Countries with Low Rose Gold Prices
Below is a table listing countries where rose gold is relatively more affordable. Factors affecting these prices may include local gold production, economic conditions, and currency exchange rates.
|
Country/Region |
Price per Gram (USD) |
|---|---|
|
South Africa |
$40 – $45 |
|
Turkey |
$38 – $44 |
|
Indonesia |
$35 – $42 |
|
Thailand |
$36 – $43 |
|
Vietnam |
$37 – $44 |
These prices are approximate and subject to change based on various factors, such as market dynamics and the purity of the gold alloy. It’s recommended to verify with local jewelers or financial institutions for the most accurate and current pricing.
Rose Gold Official Outlets Globally
The table below provides a list of countries with official outlets for purchasing this metal. These outlets follow specific rules and regulations to ensure the quality and authenticity of their rose gold products.
|
Country |
Official Outlets |
Regulations and Rules |
|---|---|---|
|
United States |
Tiffany & Co., Cartier, Kay Jewelers |
Products must be stamped with purity marks; strict adherence to Federal Trade Commission guidelines. |
|
United Kingdom |
Harrods, Goldsmiths, H. Samuel |
Compliance with the UK Hallmarking Act; all jewelry must carry a certified hallmark. |
|
Canada |
Birks, Peoples Jewellers, Ben Moss |
Items labeled with karat fineness; adherence to the Competition Bureau’s metal marking guidelines. |
|
Australia |
Michael Hill, Prouds, Angus & Coote |
All gold products are hallmarked, and the Australian Competition and Consumer Commission enforces metal content accuracy. |
|
Germany |
Wempe, Christ, Meister |
Jewelry must comply with the German Hallmarking Act; purity marks are mandatory. |
|
Japan |
Tasaki, Mikimoto, Ginza Tanaka |
Products must indicate purity level; compliance with Japan’s Precious Metal Labeling Act. |
|
United Arab Emirates |
Damas, Malabar Gold & Diamonds, Pure Gold Jewellers |
Strict adherence to Dubai Central Laboratory standards; hallmarking required for all gold items. |
These outlets must follow regional regulations to maintain high standards and ensure their customers receive authentic rose gold products. It’s advisable to verify the authenticity of rose gold purchases by looking for official certifications and compliance with local rules.
Rose Gold Worldwide Selling Website URL Table
The following table highlights some popular websites where rose gold jewelry and accessories can be purchased globally. These platforms offer a wide range of rose gold products, catering to different preferences and styles:
|
Country/Region |
Website |
URL |
|---|---|---|
These websites are recommended for their reputation, range of products, and customer service. It’s always advisable to check for reviews and ratings to ensure a satisfactory shopping experience.
Recommended Books on Rose Gold
Exploring the allure and craftsmanship behind rose gold can be greatly enhanced by delving into literature that captures its historical, aesthetic, and economic significance. Below are some recommended books for enthusiasts and professionals alike:
1-“Rose Gold: The Color for Romance” by Ornella Pistilli
This gripping book explores the history and modern-day quest for gold, including the appeal of rose gold in current markets.
2-“The Art of Jewelry Design: Principles of Design, Rings & Earrings” by Elizabeth Olver
A comprehensive guide on jewelry design principles, this book offers invaluable insights into creating timeless rose gold pieces.
3-“Becoming a Supple Leopard” by Marco Ceccarelli
While primarily about exercise, this book explores the use of metals like rose gold in a broader context of human craftsmanship and the luxury market.
4-“Jewelry Concepts & Technology” by Oppi Untracht
This essential volume provides a detailed understanding of jewelry techniques, including the unique properties and appeal of rose gold.
5-“Gold: The Race for the World’s Most Seductive Metal” by Matthew Hart
A visually rich guide exploring the allure of rose gold, its romantic connotations, and its role in jewelry design.
These books offer a diverse perspective on rose gold, from technical insights to historical narratives, making them ideal resources for both novice enthusiasts and seasoned professionals in the field.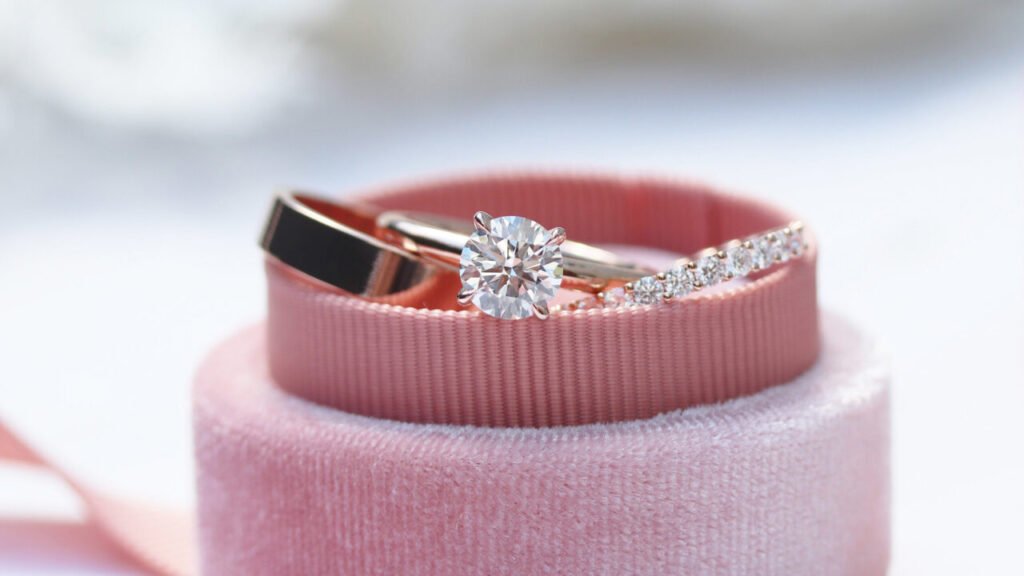
Rose Gold Web Resources
Discovering the beauty and versatility of it involves exploring various online resources that offer deep dives into this luxurious metal. Below are some web resources where enthusiasts can learn more about rose gold, its history, and its applications in jewelry design:
The Assay Office’s website provides a wealth of information about hallmarking standards, including insights into it certification.
This platform offers educational resources on various metals, including this, and supports ethical practices in the jewelry industry.
The GIA website offers comprehensive courses and articles on gemstone and metal information, providing expert insights into this jewelry.
Ideal for DIY enthusiasts, this site includes tutorials and articles that often feature its projects, allowing creatives to experiment with this metal.
With a focus on technique and craftsmanship, Ganoksin offers resources for jewelers interested in working with this, including technical articles and discussion forums.
These websites serve as valuable references for anyone interested in the unique allure of this, from amateur enthusiasts to seasoned jewelers aiming to enhance their knowledge and expertise.
Rose Gold References
For those seeking to expand their understanding and appreciation of this, both scholarly and practical resources can be invaluable. The following references provide further reading and insights into the unique qualities of this popular metal:
- “Colors of Gold: A Metallurgical Analysis” by Dr. Johan Schlamann
This academic paper delves into the chemical composition of this, detailing the specific alloying elements that give it its distinctive hue.
- “The Metalsmith’s Book of Secrets” by Alan Revere
Known for its in-depth explanations and illustrations, this book covers various techniques used in working with this, showcasing its versatility in jewelry making.
- “Adorn: A Comprehensive Guide to Jewelry” edited by Barbara Bergstein
An essential guide for any jewelry aficionado, this volume explores contemporary uses of rose gold in fine jewelry.
- “Rose Gold: A Historical Perspective” published in the Journal of Jewelry Research
This journal article offers a thorough historical analysis of its popularity through different eras, providing context for its current trends.
These references are vital resources for anyone wanting to deepen their knowledge of it, offering a blend of technical information and aesthetic considerations for its use in jewelry design.
Pros and Cons of Rose Gold
Pros:
- Unique Aesthetic Appeal: it stands out for its warm, pinkish hue that brings a romantic and vintage feel to jewelry.
- Versatility in Design: It complements various skin tones and pairs well with other metals and gemstones, allowing creative design combinations.
- Durability: With alloys like copper, it is often more durable than yellow or white gold, making it suitable for daily wear.
Cons:
- Potential for Tarnishing: The copper content in it may lead to tarnishing over time, especially in humid environments.
- Allergies: Individuals with copper sensitivities may experience allergic reactions when wearing rose gold jewelry.
- Maintenance: Like other gold alloys, rose gold requires regular cleaning and care to maintain its luster and appearance.
FAQs About Rose Gold
What is rose gold made of?
It is an alloy made primarily of gold and copper, with the pinkish color resulting from the copper content.
Is it more expensive than other gold?
This is generally priced similarly to yellow and white gold, depending on the alloy composition and karat value.
Does this fade or change color over time?
While it does not tarnish or fade like some other metals, the copper can cause slight darkening as it ages.
Can it be resized or repaired easily?
Yes, it can be resized and repaired, though it is important to consult with a jewelry professional familiar with working with this alloy.
Research Summary
The allure of it is deeply rooted in its unique color and historical significance. Recent studies show that consumer interest in it has been steadily increasing, driven by its association with luxury and timeless elegance.
Technological advancements in metallurgy have enabled jewelers to experiment with different alloy compositions, enhancing the versatility and durability of this products. Furthermore, economic analyses suggest the demand for this remains strong, particularly in markets prioritizing bespoke and custom designs.
FASHION
What is Fasion: Latest Guide Answer

What is Fashion? A Historical Overview
what is Fashion an ever-evolving cultural phenomenon that encompasses the creation, distribution, and consumption of clothing, accessories, and footwear. Fashion plays a critical role in defining personal and societal identities, influencing social behaviors, and reflecting economic, cultural, and political contexts. Throughout history, fashion has been a tool for self-expression, a status symbol, and a way of communicating one’s values, beliefs, and affiliations.
Fashion is About Style
At its core, fashion is about style, which represents the preferences of individuals or groups at a particular point in time. However, fashion also refers to the patterns of change in those styles, which are often shaped by designers, celebrities, and cultural shifts. The fashion industry has become one of the most powerful sectors of the global economy, impacting not only the clothing and textile industries but also media, advertising, and even technology.
Fashion as an Art Form
Fashion is often considered an art form due to its combination of creativity, design, and expression. Just like any other art form, fashion transcends utility and enters the realm of aesthetics, with designers acting as artists who draw inspiration from various sources, from historical influences to nature, art movements, or even political events.
The evolution of fashion mirrors the changes in society, with significant shifts reflecting broader cultural, technological, and economic transformations. Over time, fashion has evolved from practical garments to elaborate expressions of individuality and luxury. It is influenced by various aspects, including geography, climate, social status, and technological advancements.
The Rise of Fashion Industry
The development of the fashion industry as a commercial entity began in the 19th century, with figures like Charles Frederick Worth, who is often considered the first fashion designer. Worth’s establishment of a couture house in Paris in the 1850s is considered the beginning of high fashion, where elite clients could have garments custom-made to fit their tastes and needs.
The rise of mass production and the expansion of ready-to-wear clothing in the 20th century democratized fashion. In this era, the focus shifted from individualized, custom clothing to mass-produced garments, making fashion more accessible to a wider audience. Designers like Coco Chanel and Christian Dior helped define the fashion landscape, establishing iconic looks that have stood the test of time.
Fashion also started to play a critical role in social movements, such as the rise of youth subcultures in the 1960s, and the feminist movement, which challenged traditional gender norms and roles in fashion. The late 20th and early 21st centuries saw a merging of fashion and technology, with innovations such as fast fashion, the internet, and social media reshaping how people engage with and experience fashion.
Key Elements of Fashion
- Clothing: Clothing is the fundamental aspect of fashion, with various styles evolving to suit different needs, occasions, and personal expressions. From casual wear to formal attire, the choices in clothing define individual and collective identity.
- Accessories: Accessories, including jewelry, hats, bags, and scarves, often complement clothing and can transform an outfit. These items have long been used to signify wealth, status, or personal taste.
- Footwear: Shoes have always been a critical component of fashion, ranging from functional to ornamental. Footwear is often the focal point of many fashion collections, and the types of shoes a person wears can make a bold statement.
- Hairstyles & Makeup: Fashion extends beyond clothing to include personal grooming. Hairstyles and makeup trends have changed drastically over time, reflecting societal norms, technological advancements, and shifting cultural attitudes.
- Designers and Brands: Fashion is often shaped by the vision of influential designers and global brands. Designers like Alexander McQueen, Vivienne Westwood, and Jean-Paul Gaultier have all contributed significantly to the creative direction of the industry.
A Historical Overview of Fashion
To understand how fashion has evolved over time, it is important to look at key periods and movements in its history. Below is a table summarizing significant trends in fashion history:
| Period | Fashion Trends | Cultural Context |
|---|---|---|
| Ancient Civilizations | Simple garments, draped clothing like togas and tunics, jewelry as status symbols | Social hierarchy, religion, and climate play a major role in dress |
| Middle Ages (5th-15th century) | Long flowing robes, elaborate embroidery, use of fur for the elite | Medieval social classes, religious influence on dress |
| Renaissance (14th-17th century) | Corsets, ruffled collars, elaborately decorated fabrics, lace | Economic prosperity, art, and exploration led to flamboyant styles |
| 18th Century (Baroque & Rococo) | Elaborate gowns, powdered wigs, dresses with wide skirts (hoops) | Age of Enlightenment, aristocratic luxury and extravagance |
| Victorian Era (19th century) | Bustles, corsets, long skirts, top hats, elaborate bonnets | Industrial Revolution, strict social codes, modesty in women’s fashion |
| Roaring Twenties (1920s) | Flapper dresses, bobbed hair, shorter hemlines, cloche hats | The Jazz Age, women’s emancipation, and the rise of the modern woman |
| Post-War (1940s-50s) | New Look by Christian Dior, hourglass silhouettes, full skirts, suits for men | Economic recovery, rise of the middle class, and societal conservatism |
| 1960s | Mini skirts, psychedelic prints, and mod style | Counterculture, sexual revolution, and youth-driven movements |
| 1970s | Bell-bottoms, boho chic, platform shoes, disco style | Political activism, civil rights movements, and the rise of pop culture |
| 1980s | Power suits, oversized silhouettes, neon colors, and punk influences | Economic prosperity, celebrity-driven culture, and tech innovation |
| 1990s | Minimalism, grunge fashion, slip dresses, baggy pants | Youth rebellion, the internet age, and a shift towards individuality |
| 2000s-2010s | Skinny jeans, fast fashion, athleisure, streetwear | Social media, celebrity influence, and the dominance of fashion brands |
| 2020s | Sustainability, gender-neutral clothing, vintage, and upcycled fashion | Environmental concerns, inclusive fashion, and the digital revolution |
Latest Research Summary
Artificial Intelligence and Fashion Design
Researchers have developed generative AI models to transform fashion design processes. These models utilize latent diffusion techniques to create high-quality images from text and sketches, enhancing design workflows.
Sustainable Fashion Practices
Studies have highlighted the environmental impact of fast fashion, noting a 50% increase in polyester-based materials in landfills over the past two decades. This research underscores the need for sustainable practices and circular economies in the fashion industry.
Consumer Behavior and Digital Trends
The fashion industry has observed shifts in consumer behavior, with movements like “deinfluencing” encouraging sustainable consumption and authentic luxury. Brands are leveraging social media platforms to engage with Gen Z and millennial audiences, adapting to evolving digital trends.
Technological Innovations in Fashion
Advancements in wearable technology, such as augmented reality glasses and mixed reality headsets, have gained attention. These innovations blend digital experiences with physical fashion, offering new consumer interactions.
These developments reflect the fashion industry’s ongoing efforts to integrate technology, promote sustainability, and adapt to changing consumer behaviors.
Fashion FAQs – Short Answers
- What is fashion?
Fashion refers to popular styles in clothing, accessories, and beauty trends, reflecting individual and cultural identity. - How does fashion impact society?
Fashion shapes social norms, identities, and cultural movements, often acting as a form of self-expression. - Who sets fashion trends?
-
What is haute couture?
-
- What’s the difference between haute couture and ready-to-wear?
Haute couture is bespoke and exclusive, while ready-to-wear is mass-produced for the general public. - How has fashion evolved?
Fashion has evolved with cultural, political, and technological changes, from medieval robes to modern, fast fashion. - What are key fashion movements?
Notable movements include the French Revolution, 1920s flappers, punk fashion, and minimalism in the 1990s. - What is fast fashion?
Fast fashion is the quick, mass production of inexpensive clothing based on current trends. - Why is sustainability important in fashion?
Sustainability reduces the fashion industry’s environmental and social impact by promoting eco-friendly practices. - What’s the difference between fashion and style?
Fashion refers to current trends, while style is a personal expression of how someone wears them. - How do fashion designers influence trends?
Designers set trends through their collections, often showcased at fashion weeks and collaborations. - What is the role of fashion weeks?
Fashion weeks are events where designers present new collections that set trends for upcoming seasons. - What is streetwear?
Streetwear is casual, urban clothing influenced by skateboarding and hip-hop culture, often with a rebellious vibe. - How can I develop my personal style?
Experiment with different looks, find what suits you, and express your personality through your clothes. - What is the future of fashion?
Fashion’s future will focus on sustainability, inclusivity, and new technologies like AI and virtual fashion.
FASHION
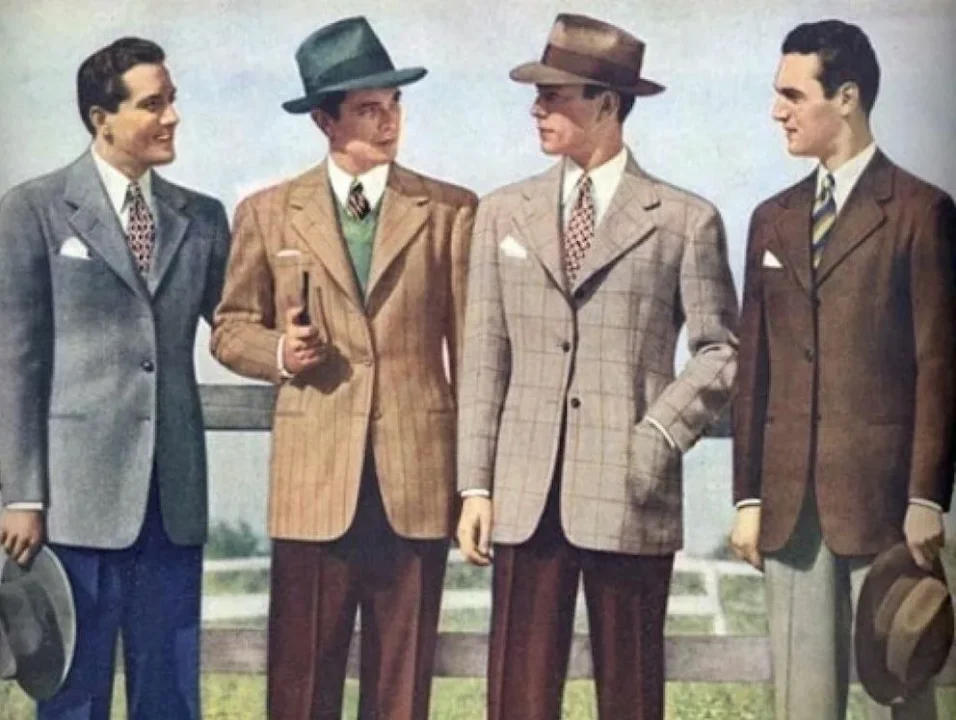
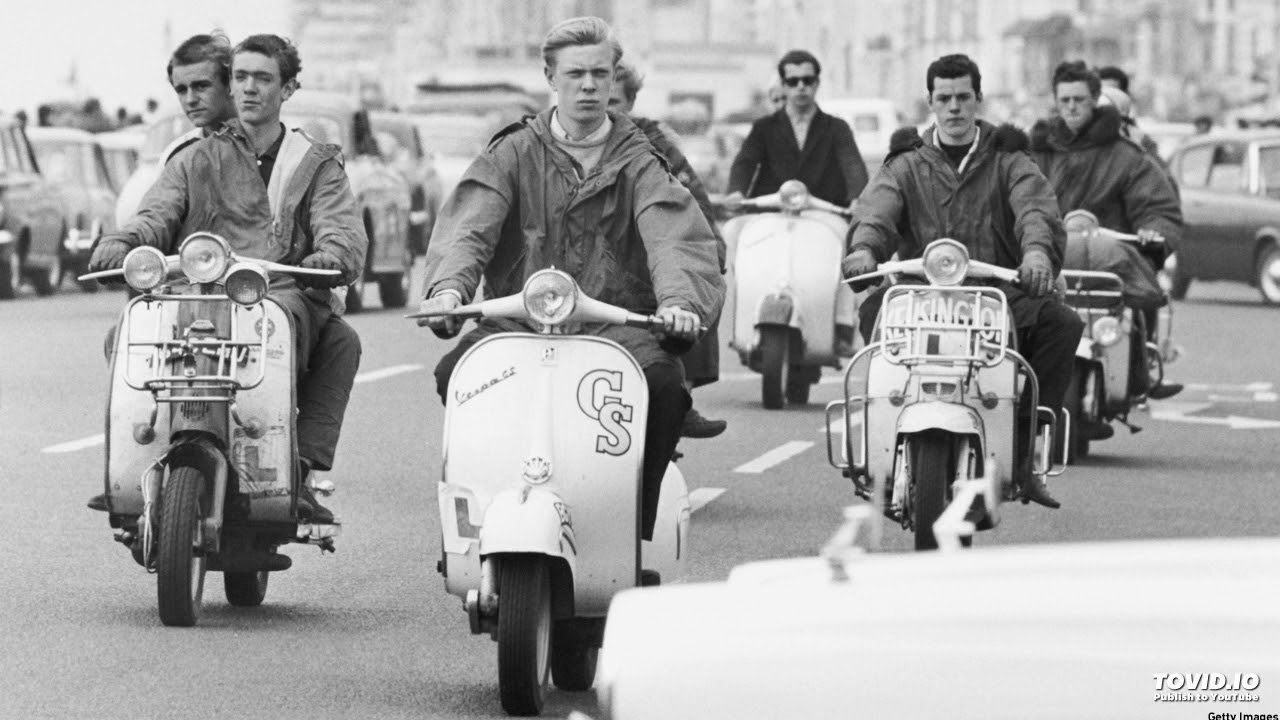
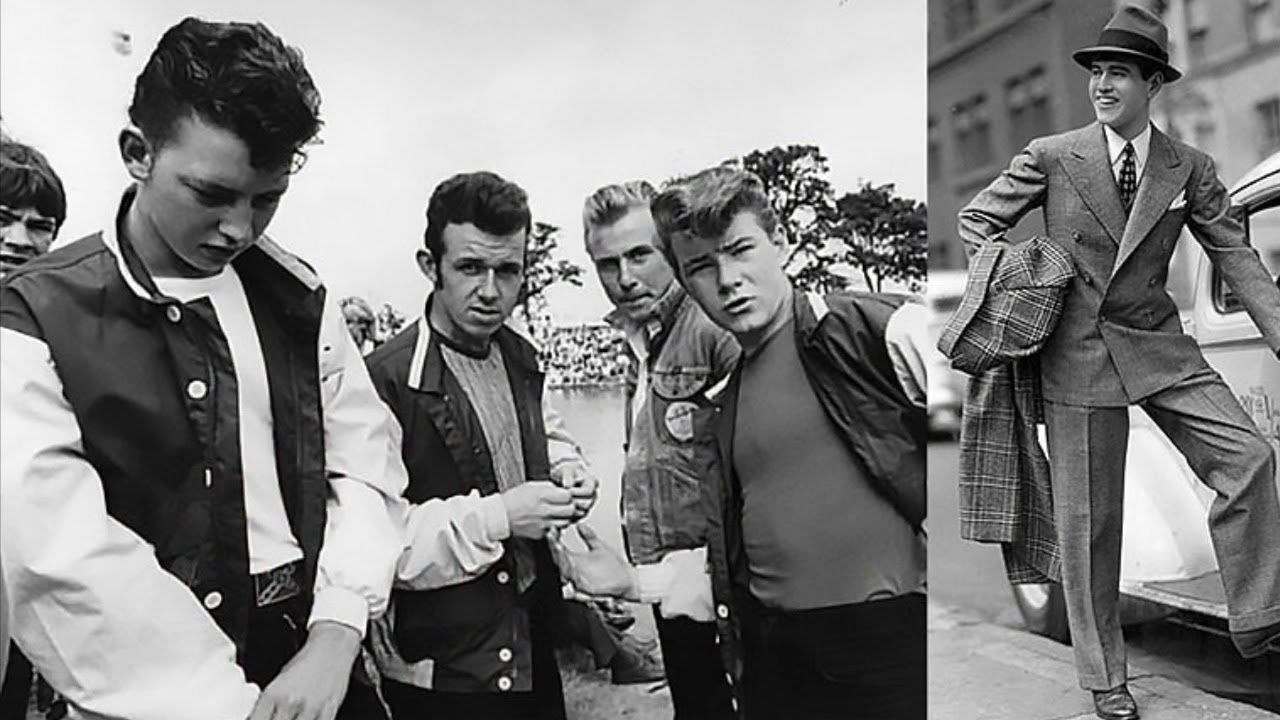
1960s Fashion Men: Old Memories
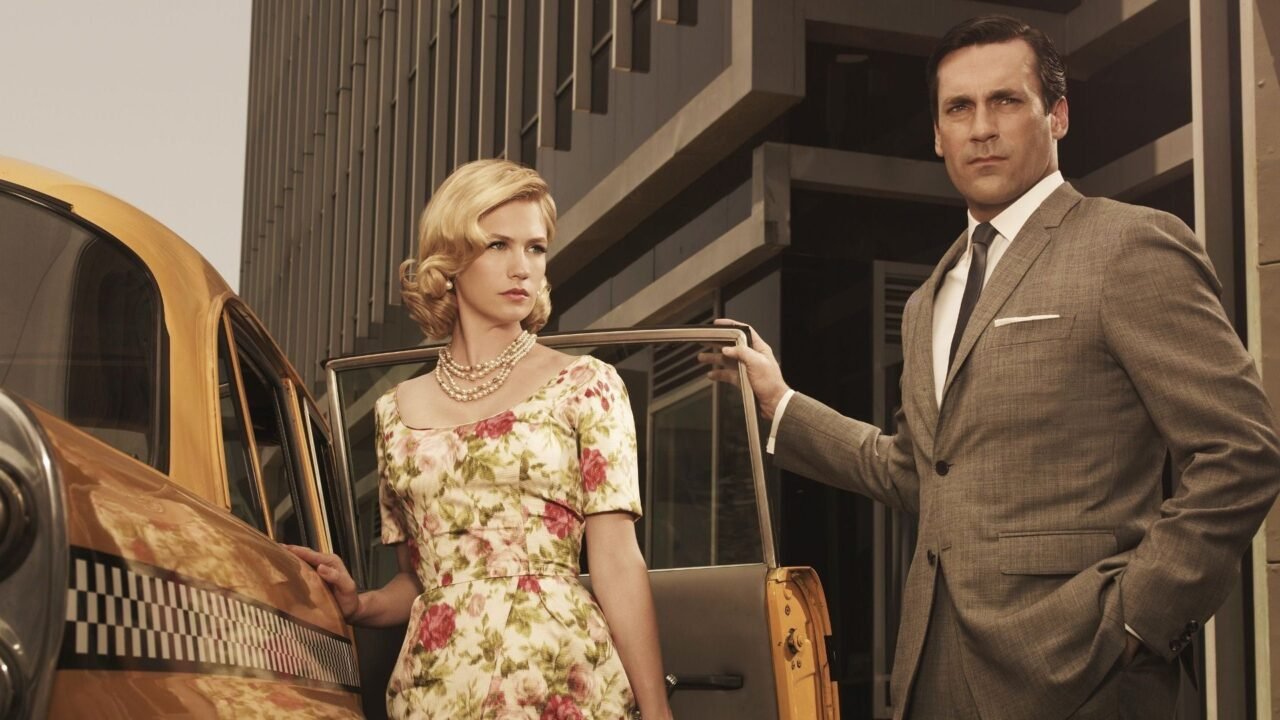

1960s Men’s Fashion: A Decade of Style Transformation
1960s fashion men marked a turning point in men’s fashion, reflecting a mix of traditional and revolutionary styles. Influenced by cultural movements, social change, and iconic figures, the decade saw a shift from conservative tailoring to experimental and vibrant looks. Here’s a comprehensive look at 1960s men’s fashion.
1. Early 1960s: Clean-Cut Sophistication
The beginning of the decade maintained the conservative styles of the 1950s:
- Suits: Slim-cut single-breasted suits in muted tones like gray, navy, and black were staples. These suits were paired with narrow ties and crisp white shirts, creating a polished and professional look.
- Casual Wear: Men opted for neatly pressed trousers, button-down shirts, and v-neck sweaters. The Ivy League look, characterized by loafers and cardigans, was highly popular.
- Accessories: Pocket squares, fedora hats, and leather dress shoes completed the look.
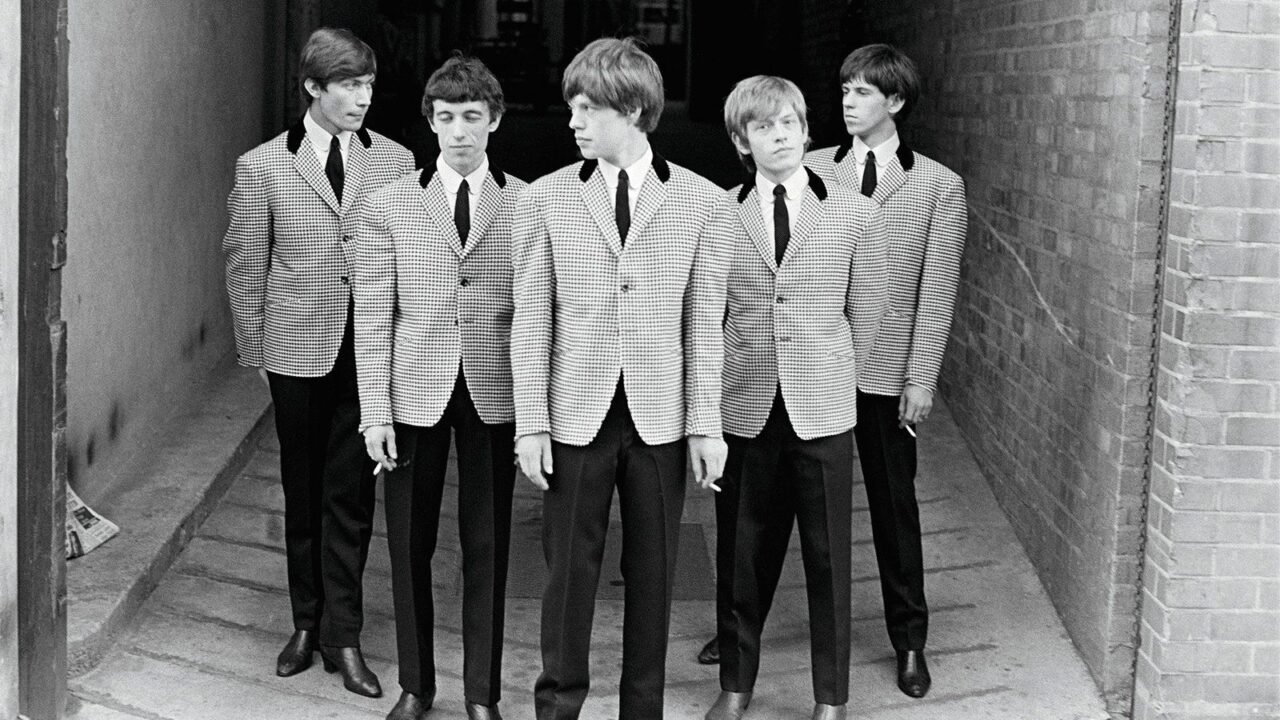
2. Mid-1960s: The Mod Movement
Inspired by the British Mod subculture, men embraced sharp, tailored clothing with bold, geometric designs:
- Slim Suits: Suits became tighter and shorter, with narrow lapels and trousers that broke at the ankle.
- Colorful Choices: Bright colors like mustard yellow, green, and burgundy were introduced, a stark contrast to the muted tones of the early ’60s.
- Turtlenecks: Often paired with blazers, turtlenecks replaced traditional shirts for a modern, sleek look.
- Footwear: Chelsea boots, popularized by The Beatles, became a must-have.
3. Late 1960s: The Counterculture Influence
As the decade progressed, the counterculture movement brought a wave of bohemian and hippie styles:
- Relaxed Fits: Loose, unstructured clothing like bell-bottom jeans and tunics became the norm.
- Patterns and Prints: Tie-dye shirts, Paisley prints, and floral patterns became symbols of self-expression.
- Outerwear: Suede jackets with fringe detailing and leather coats were popular.
- Ethnic Elements: Men embraced global influences, wearing caftans, ponchos, and embroidered shirts.
4. Key Trends Throughout the Decade
- Hairstyles: Early in the decade, men favored clean-cut, side-parted hair. By the late ’60s, longer, shaggy hairstyles inspired by rock musicians became the norm.
- Accessories: Aviator sunglasses, wide belts, and leather bracelets complemented the evolving looks.
- Influence of Icons: Celebrities like John F. Kennedy, The Beatles, and Jimi Hendrix played significant roles in shaping men’s fashion.
5. Materials and Fabrics
- Wool and tweed dominated the early years for formalwear.
- Denim became a staple for casual outfits, especially among younger men.
- Suede and velvet introduced texture and sophistication to modern and hippie styles.
6. Legacy of 1960s Men’s Fashion
The decade laid the foundation for modern men’s fashion by promoting individuality and experimentation. It blurred the lines between formal and casual wear, giving rise to freedom of self-expression in style.
Here are the five most memorable fashion trends for men from the 1960s:
1. The Mod Suit
- Popularized by British subculture and The Beatles, the Mod suit was slim-fitting, with narrow lapels and trousers that ended at the ankle.
- Colors ranged from classic neutrals to bold tones like burgundy and green, often paired with turtlenecks for a sleek, modern look.
- Accessories like Chelsea boots and skinny ties completed this iconic ensemble.
2. Ivy League and Preppy Style
- Early in the decade, Ivy League-inspired outfits dominated, featuring blazers, button-down shirts, chinos, and loafers.
- This style represented clean-cut sophistication and was embraced by professionals and students alike.
3. Leather Jackets
- Inspired by rock ‘n’ roll culture and figures like Elvis Presley, leather jackets became a symbol of rebellion and masculinity.
- Paired with denim jeans and white T-shirts, the look exuded effortless cool and a rugged attitude.
4. Hippie and Bohemian Styles
- In the late 1960s, the counterculture movement introduced loose-fitting clothing, such as bell-bottom jeans, tie-dye shirts, and ethnic-inspired garments like caftans and ponchos.
- Floral patterns and fringe detailing on jackets became symbolic of the era’s free-spirited ethos.
5. Military-Inspired Clothing
- With growing anti-establishment sentiments, men adopted military jackets, often styled casually with jeans and boots.
- Olive green, khaki, and camouflage patterns became staples, blending utility with style.
These trends collectively represent the diversity and transformation of 1960s men’s fashion, from the tailored elegance of Mod styles to the carefree, expressive hippie movement.
Detailed FAQs About 1960s Men’s Fashion
What influenced men’s fashion in the 1960s?
Men’s fashion in the 1960s was heavily influenced by cultural movements, music, and global politics. The Mod subculture, spearheaded by British bands like The Beatles and The Rolling Stones, introduced tailored suits and bold colors. Meanwhile, the counterculture movement of the late 1960s brought loose, bohemian styles inspired by the hippie ethos.
What was the Mod look for men?
The Mod look featured slim-cut suits with narrow lapels and trousers, often paired with button-down shirts or turtlenecks. Accessories included skinny ties, Chelsea boots, and round sunglasses. It was a clean, sharp aesthetic popularized in London during the early part of the decade.
What types of suits were popular for men in the 1960s?
Men’s suits in the 1960s varied based on the style movement:
- Mod suits were slim and minimalist.
- Traditional Ivy League suits included blazers and chinos with a preppy flair.
- Late 1960s suits had wider lapels and were often brightly colored or patterned, influenced by the psychedelic movement.
How did the counterculture movement affect men’s fashion?
The counterculture movement introduced casual, expressive styles, such as tie-dye shirts, bell-bottom jeans, and fringed jackets. Accessories like beads and headbands became common, reflecting the era’s emphasis on individuality and freedom.
What accessories were common in 1960s men’s fashion?
Popular accessories included skinny ties, leather belts, round sunglasses (à la John Lennon), and hats like fedoras or berets. Footwear varied from sleek Chelsea boots to casual loafers and leather sandals during the hippie movement.
What hairstyles were trendy for men in the 1960s?
- Early 1960s: Short, neat hairstyles like the Ivy League cut were prevalent.
- Mid-1960s: The Beatles popularized longer, shaggy cuts.
- Late 1960s: Men embraced longer, unkempt hair and even afros as counterculture influences grew.
Were leather jackets popular in the 1960s?
Yes, leather jackets became a staple, symbolizing rebellion and masculinity. They were often paired with jeans and white T-shirts, popularized by icons like Elvis Presley and Marlon Brando.
What role did music play in 1960s men’s fashion?
Music had a profound impact on men’s fashion. British bands influenced Mod styles, while artists shaped the hippie movement like Jimi Hendrix and The Grateful Dead, whose bohemian attire inspired millions.
What fabrics and patterns were common in 1960s menswear?
Popular fabrics included cotton, tweed, and polyester. Patterns ranged from classic pinstripes in suits to bold florals, paisleys, and geometric prints in casual clothing during the psychedelic era.
What shoes defined 1960s men’s fashion?
- Chelsea boots: Sleek and versatile, ideal for Mod styles.
- Loafers: A staple in Ivy League and preppy looks.
- Sandals and moccasins: Popular in the counterculture movement.
How did military styles influence 1960s fashion for men?
1960s Fashion Men Military surplus items like olive-green jackets and camouflage patterns became popular, reflecting the political climate and anti-establishment sentiment of the decade.
Why are 1960s men’s fashions still relevant today?
Many 1960s styles, like tailored Mod suits and casual bohemian looks, continue to inspire contemporary fashion. Retro trends often resurface, with designers drawing on the diverse aesthetics of the era for modern collections.
FASHION
latest fashion trends:Sustainability Nostalgia
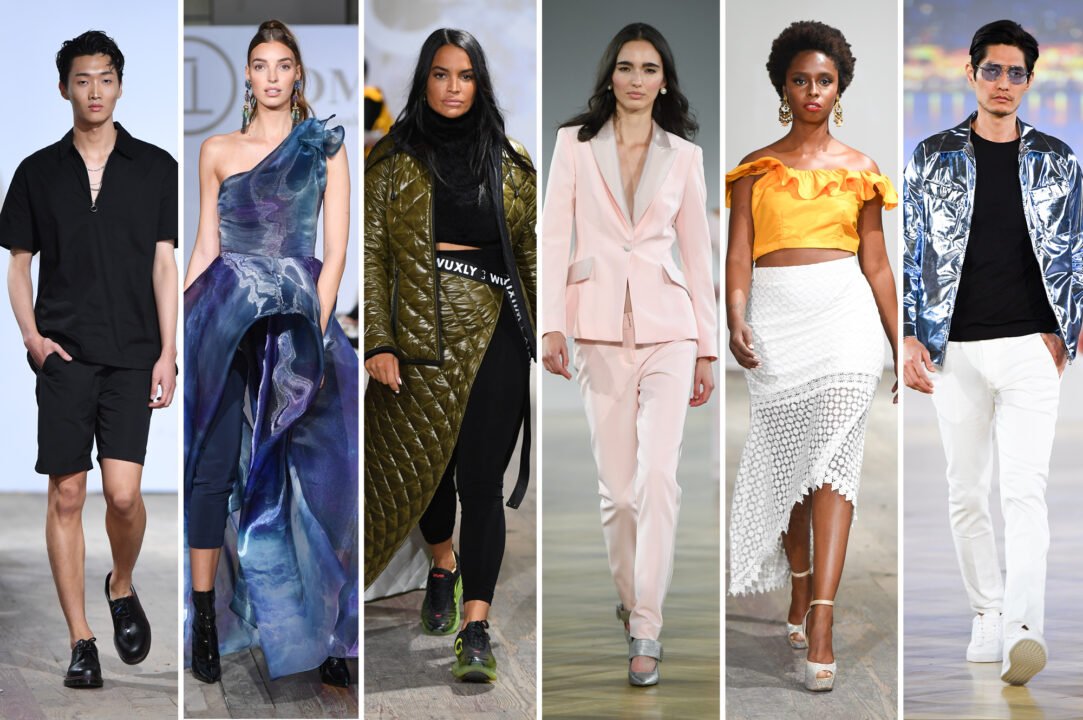

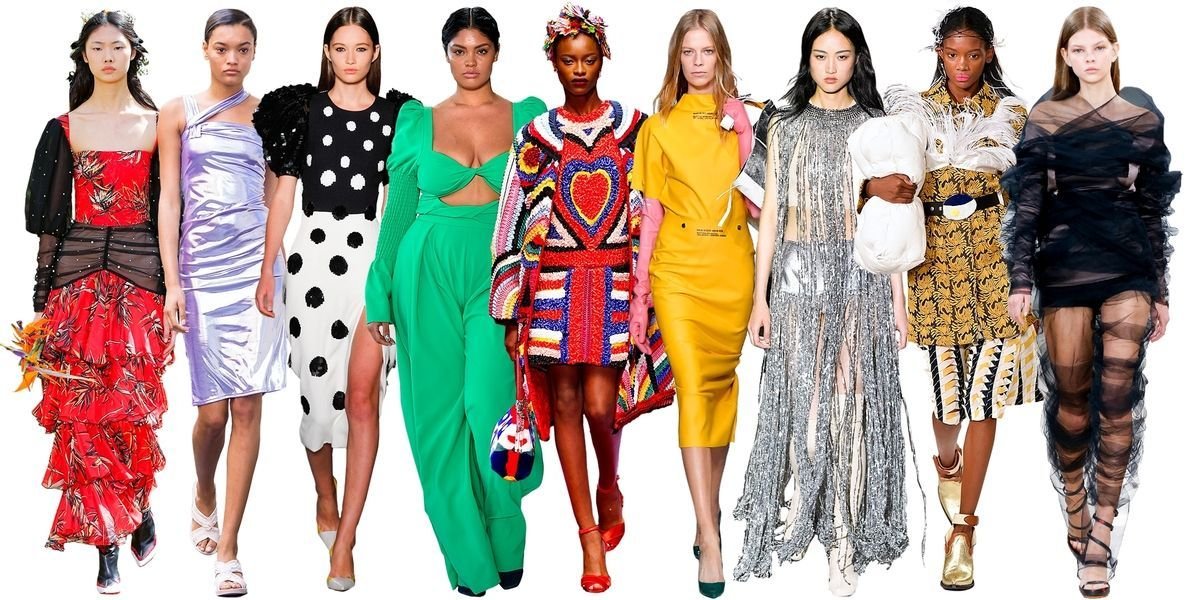
The Latest Fashion Trends for 2024
latest fashion trends is an ever-evolving art form, and as we step into 2024, the trends reflect a dynamic combination of nostalgia, futuristic elements, and a shift towards sustainable practices. From bold statements to refined minimalism, here’s a comprehensive look at the latest fashion trends that are dominating the year.
1. Sustainable and Ethical Fashion
In 2024, sustainability continues to be at the forefront of fashion. Eco-friendly fabrics like organic cotton, recycled polyester, and bamboo are making their way into the mainstream. Consumers are increasingly aware of the environmental impact of their clothing choices, leading to a rise in brands that prioritize ethical production and transparency in their supply chains. Slow fashion, which emphasizes quality over quantity, is also gaining more attention as people move away from fast fashion practices【576†source】【577†source】.
2. Tech-Infused Fashion
The intersection of technology and fashion is no longer just a futuristic concept—it’s becoming reality. In 2024, smart fabrics and wearable tech are set to be more integrated into everyday wear. Clothes with built-in LED lights, temperature-regulating fabrics, and even those that can change color based on environmental factors are pushing the boundaries of what we expect from clothing. This trend reflects a growing desire for innovation that combines utility with style【576†source】.
3. Gender-Neutral Clothing
Gender-neutral fashion continues to thrive in 2024, with a focus on inclusivity and self-expression. More brands are designing clothes that break away from traditional gender norms, offering styles that are versatile and can be worn by anyone. This trend celebrates individuality and allows people to wear what makes them feel confident, regardless of societal expectations. Expect to see more unisex clothing, oversized silhouettes, and fluid lines in both casual and formal wear【576†source】.
4. Bold Colors and Patterns
While neutrals have dominated recent years, 2024 is all about making a statement with bold colors and eye-catching patterns. Bright neon hues, particularly greens, pinks, and blues, are making a comeback, alongside vibrant prints like geometric patterns, florals, and animal prints. Fashion lovers can expect a mix of color blocking and abstract designs that create striking visual contrasts, perfect for standing out in a crowd【577†source】.
5. Techno-Styles and Futuristic Looks
Futuristic aesthetics are taking center stage in 2024, with metallics, holographics, and experimental shapes dominating the runway. Techno-inspired fashion features sleek lines, reflective materials, and outfits that seem to transcend traditional boundaries. These styles often include elements like structured jackets, iridescent accessories, and sculptural footwear, aiming to evoke a sense of space-age sophistication【576†source】.
6. Retro Revival: 90s and Y2K Trends
Nostalgia is a strong force in 2024, with fashion looking back to the late ’90s and early 2000s for inspiration. Chunky sneakers, oversized graphic tees, low-rise jeans, and bucket hats are making a return. The Y2K aesthetic, characterized by metallic fabrics, mini skirts, and bold prints, is especially popular, blending playful elements with modern-day twists【577†source】.
7. Athleisure and Sporty Styles
Athleisure, which combines comfort with style, continues to dominate in 2024. Whether it’s oversized sweatshirts, leggings, or sneakers, sporty styles are being elevated with high-fashion details. Expect to see luxury brands integrating sportswear into their collections, offering garments that seamlessly transition from the gym to a night out. This trend represents a demand for versatility, as people seek clothing that adapts to their dynamic lifestyles【576†source】【577†source】.
8. Maximalism: Layered and Exaggerated Fashion
After years of minimalist fashion, maximalism is making a huge return. This trend encourages wearing bold patterns, textures, and accessories all at once, creating an eclectic, layered look. Think oversized coats, statement jewelry, and mixing various textures and prints for a visually exciting effect. Maximalism embraces individuality, encouraging people to have fun with fashion by wearing what they love without limitations【576†source】.
9. Refined Tailoring
On the other end of the spectrum, we see a resurgence of sharp, sophisticated tailoring. Suits are getting slimmer and more fitted, with bold cuts and structured designs. Blazers and trousers are especially being reimagined with modern details, such as asymmetric cuts and metallic finishes. This trend is favored by those who enjoy a more polished, professional look while maintaining a fashion-forward edge【577†source】.
10. Footwear: From Chunky to Sleek
Footwear trends in 2024 include both extremes. Chunky sneakers and platform shoes are still very much in style, offering comfort and a bold fashion statement. On the flip side, sleek, minimalist footwear with clean lines and neutral colors are also gaining popularity. Think simple leather boots, low-profile sneakers, and elegant stilettos for a more refined look【576†source】.
Summary
Fashion in 2024 is all about blending innovation, nostalgia, and sustainability. From the bold, colorful styles inspired by past decades to the futuristic designs made possible by technology, there’s a trend for every type of fashion lover. Whether you’re embracing the maximalism movement or opting for a more minimalist, sustainable wardrobe, the key is to stay true to your own personal style and experiment with the latest trends that feel right for you.
Sources:
-

 TECH8 months ago
TECH8 months agoiPhone 16 Pro Max VS iPhone 16 Pro: Features and Insights (2024-2025)
-

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months agoMaria Taylor’s Husband: Jonathan Lee Hemphill’s Job, Family, and Kids Explained
-

 FASHION5 months ago
FASHION5 months agoOld-Fashioned: Styles Across Generation
-

 SEO6 months ago
SEO6 months agoBest website platform for seo: top 5 popular websites, 1-book, 25 Top Free SEO Tools,
-

 TECH8 months ago
TECH8 months ago2025 mercedes-benz c-class images:
-

 TECH5 months ago
TECH5 months agoNew Innovations in Technology: The Future
-

 SEO6 months ago
SEO6 months agoGoogle Ranking Factors: top 50 factors
-

 SEO6 months ago
SEO6 months agoHow to Write an Article with AI: According to the google requirements ai article book